Bringing a newborn puppy into your home is an exciting and joyful experience, but it also comes with a lot of responsibility and care.
Bringing a new puppy into your home is an exciting and joyful experience, but it also comes with a lot of responsibility. Proper care is essential to ensure that your puppy grows into a healthy, well-adjusted adult dog. This guide will take you through the key stages of puppy development, from newborn to adulthood, and provide comprehensive advice on feeding, training, socialization, health care, and more.
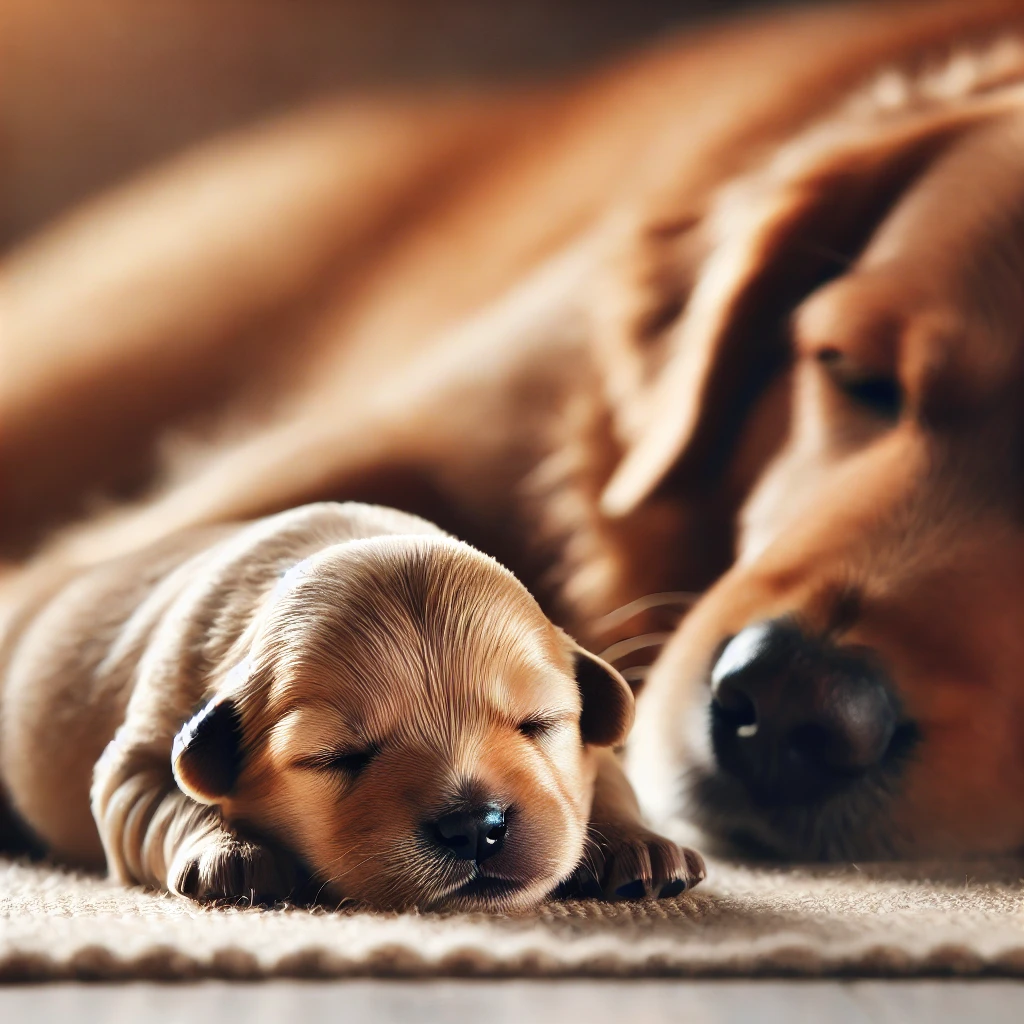

Newborn Stage (0-8 Weeks):
- Nutrition: During the first few weeks of life, puppies are entirely dependent on their mother’s milk, which provides all the necessary nutrients for growth. If the mother is not available, a vet should be consulted to provide an appropriate milk replacement formula.
- Development: Newborn puppies are born with their eyes and ears closed. They rely on their sense of touch and smell to find their mother. By the third week, their eyes and ears begin to open, and they start exploring their environment.
- Health Care: It’s crucial to monitor the puppies for signs of illness, such as lethargy, difficulty nursing, or abnormal crying. A vet should check the puppies during this stage to ensure they are developing normally.
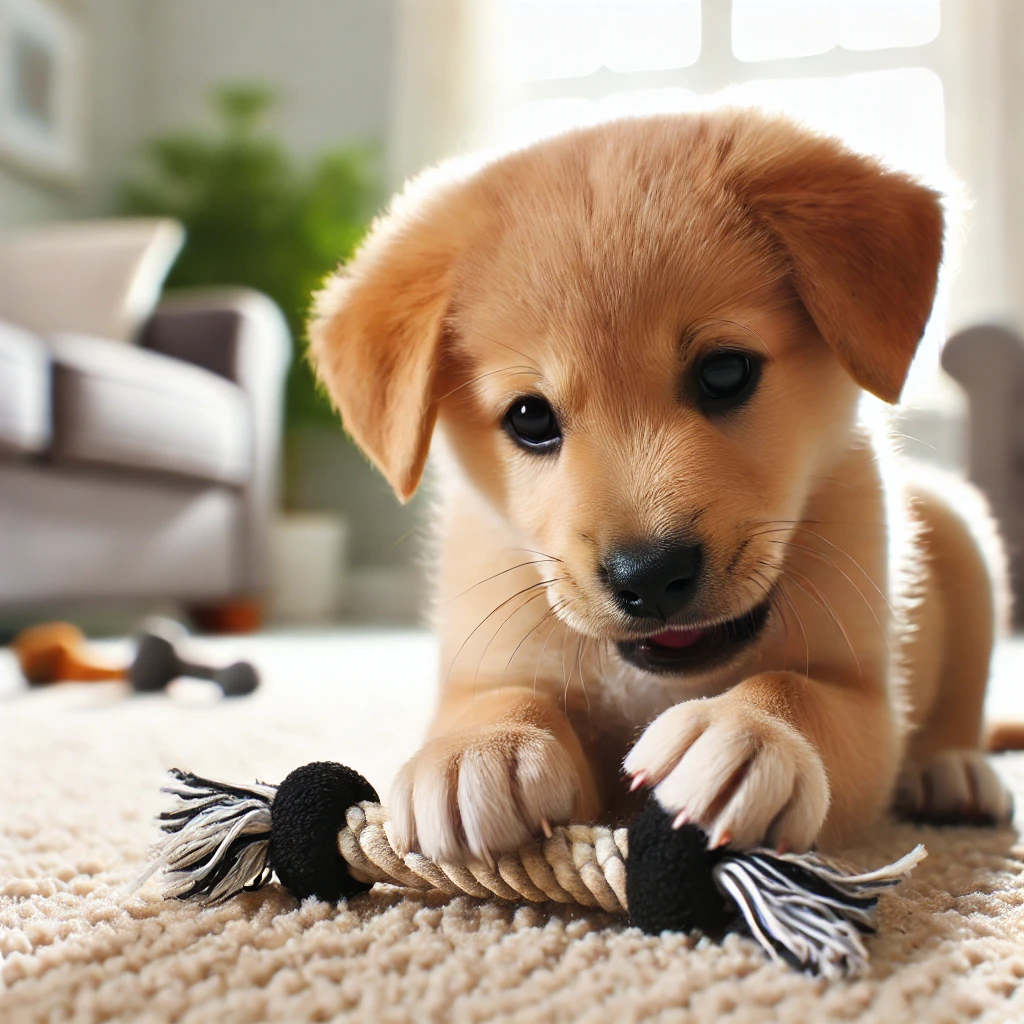

Early Socialization (3-8 Weeks):
- Social Interaction: This is a critical period for socialization. Puppies learn to interact with their littermates and mother, which helps them develop important social skills. They also begin to explore their environment and interact with humans.
- Introduction to Solid Food: Around the fourth week, puppies can start eating soft, solid food in addition to nursing. Gradually, they will begin to rely more on solid food as they wean off their mother’s milk.
- Basic Training: Gentle handling by humans is essential during this stage to help puppies become comfortable with people. Simple commands like “come” and “sit” can be introduced in a playful manner.
Puppyhood (8 Weeks – 6 Months):
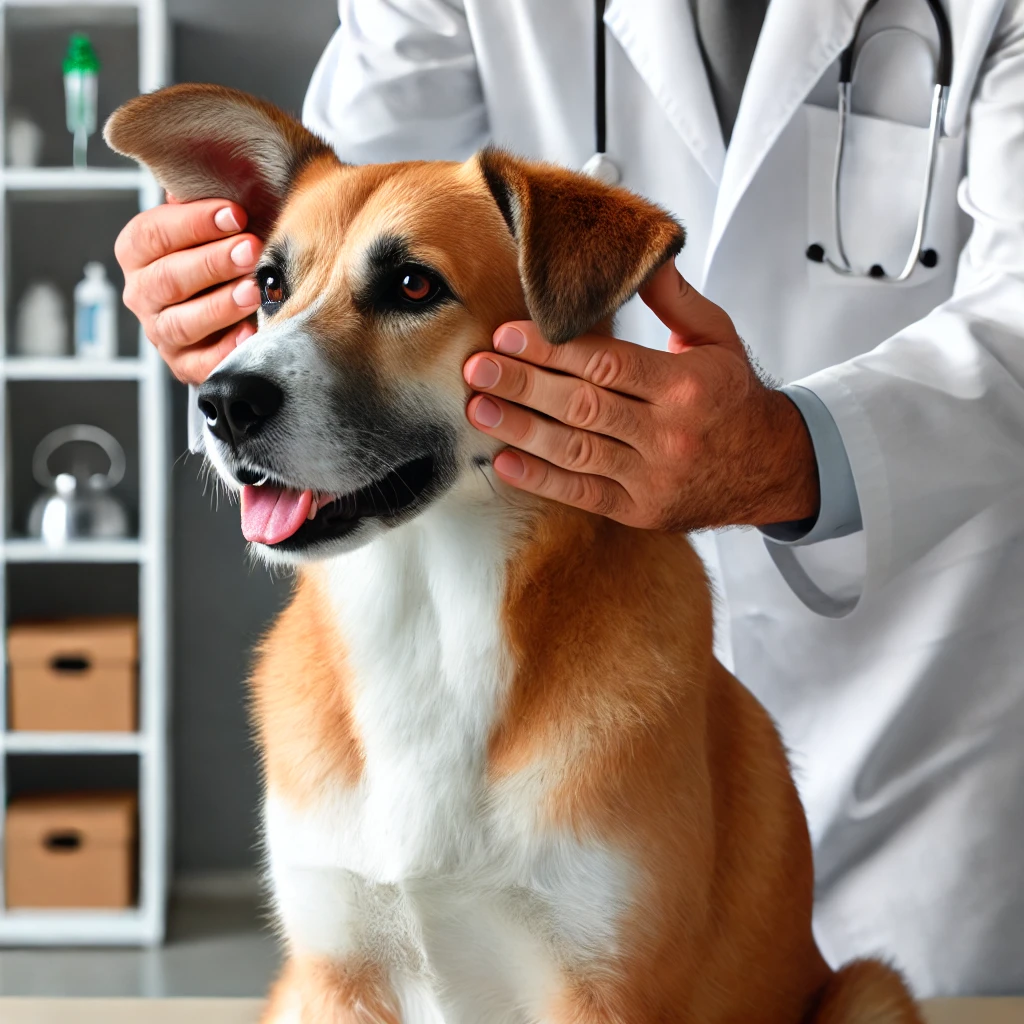
- Vaccinations and Vet Visits: By eight weeks, puppies should begin their vaccination schedule, starting with shots for distemper, parvovirus, and other common diseases. Regular vet visits are essential for monitoring growth and overall health.
- Feeding: Puppies need a high-quality puppy food that supports their rapid growth. Feeding should be done multiple times a day, with portion sizes adjusted according to the puppy’s size and breed.
- Teething: Puppies begin teething around three to four months old, leading to a desire to chew on things. Providing appropriate chew toys is essential to protect household items and support dental health.
- Socialization and Training: Continued socialization is crucial during this period. Puppies should be exposed to different people, animals, and environments to build confidence. Basic obedience training should also be a priority, focusing on commands like “sit,” “stay,” “down,” and “leave it.”
Adolescence (6 Months – 1 Year):
- Nutrition: As puppies approach six months, their growth rate begins to slow, and their feeding schedule can be adjusted to two meals per day. Transitioning to adult dog food should be done gradually to avoid digestive issues.
- Behavioral Changes: Adolescence is often marked by increased energy and testing boundaries. Consistent training and exercise are important to manage behaviors like jumping, digging, and barking.
- Exercise Needs: Adolescent dogs have high energy levels and require regular physical activity. Daily walks, playtime, and mental stimulation are essential to prevent boredom and destructive behaviors.
- Spaying/Neutering: Many vets recommend spaying or neutering around six months of age, depending on the breed and health of the puppy. This procedure can help prevent certain health issues and reduce unwanted behaviors.
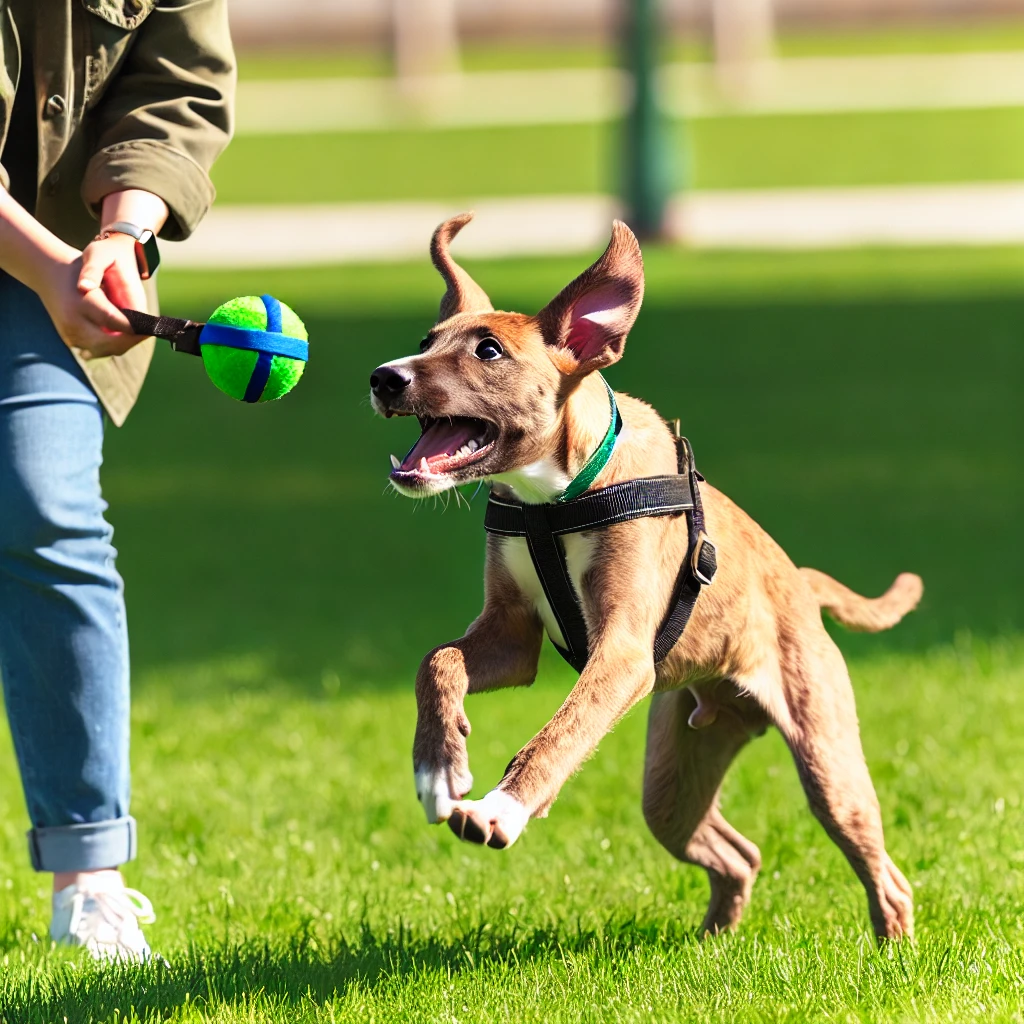
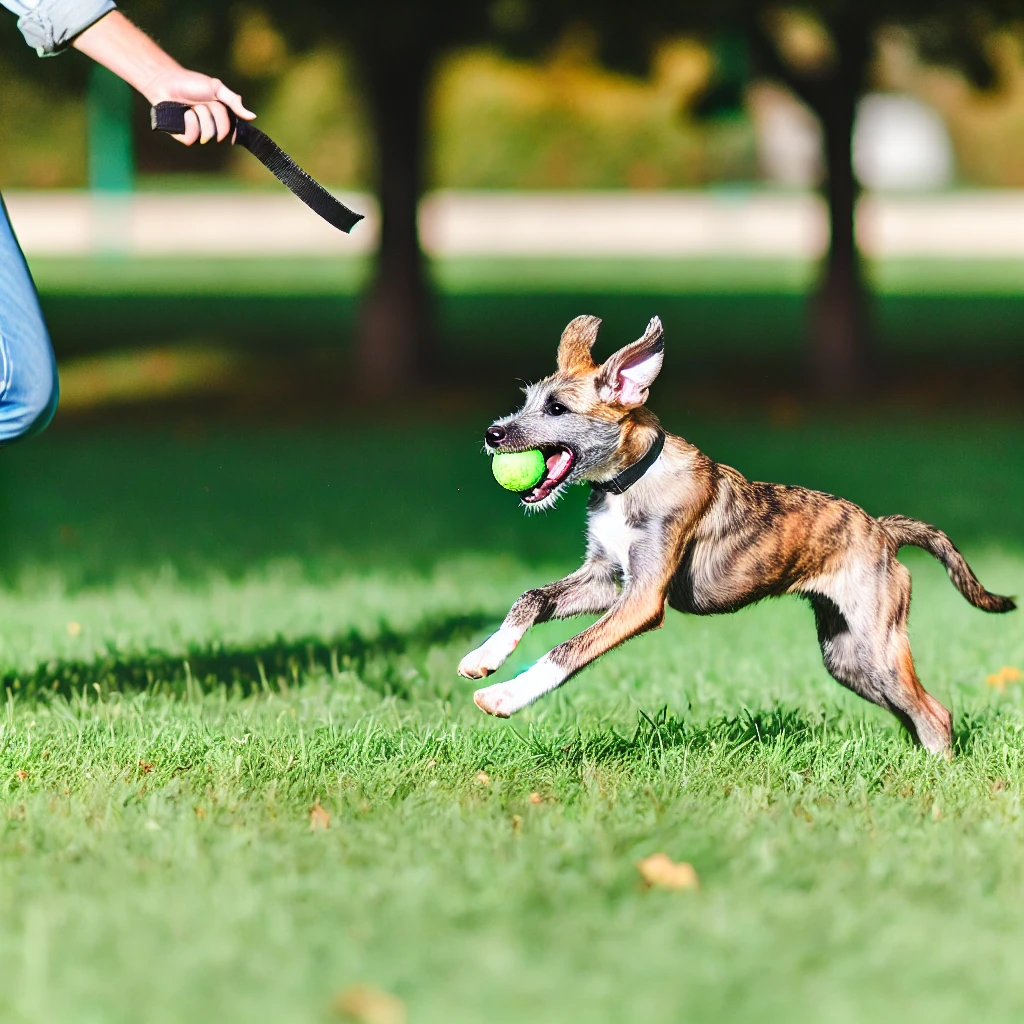


Adulthood (1 Year and Beyond):
- Health Care: Adult dogs should have regular vet check-ups, at least once a year, to monitor their health and update vaccinations. Dental care, including regular brushing and professional cleanings, is important to prevent dental disease.
- Nutrition: By adulthood, dogs should be eating a well-balanced diet appropriate for their size, breed, and activity level. Overfeeding should be avoided to prevent obesity, which can lead to various health problems.
- Exercise and Mental Stimulation: Adult dogs need consistent exercise to maintain physical health and mental well-being. Activities like fetch, agility training, and puzzle toys can keep them engaged and happy.
- Continued Training: Even as adults, dogs benefit from ongoing training to reinforce good behavior and address any emerging issues. Advanced obedience training or fun activities like agility or scent work can be introduced to challenge them mentally.
Common Health Concerns Throughout Life:
- Parasites: Regular deworming and flea prevention are essential throughout a dog’s life. Puppies are particularly vulnerable, but adult dogs also need protection from parasites.
- Vaccinations: Keeping up with vaccinations is crucial to protect your dog from preventable diseases. Your vet will recommend a schedule based on your dog’s age, lifestyle, and health.
- Dental Care: Dental health is often overlooked but is crucial for your dog’s overall well-being. Regular brushing and dental chews can help prevent plaque buildup and gum disease.
Building a Strong Bond:
- Positive Reinforcement: Use positive reinforcement techniques such as treats, praise, and play to build a strong bond with your dog. Consistent training and clear communication are key to a happy, well-behaved pet.
- Quality Time: Spending quality time with your dog through walks, play, and cuddling strengthens your relationship and contributes to their emotional well-being.
- Understanding Their Needs: Each dog is unique, and understanding your dog’s specific needs, whether it’s exercise, mental stimulation, or affection, will help you provide the best care possible.
Conclusion: Raising a puppy requires dedication, patience, and a lot of love. By following the guidelines in this comprehensive care guide, you can ensure that your puppy grows into a healthy, happy adult dog. Remember, the effort you put into your puppy’s care in these early stages will set the foundation for a lifelong bond and a well-adjusted canine companion.


